What is Product life cycle?
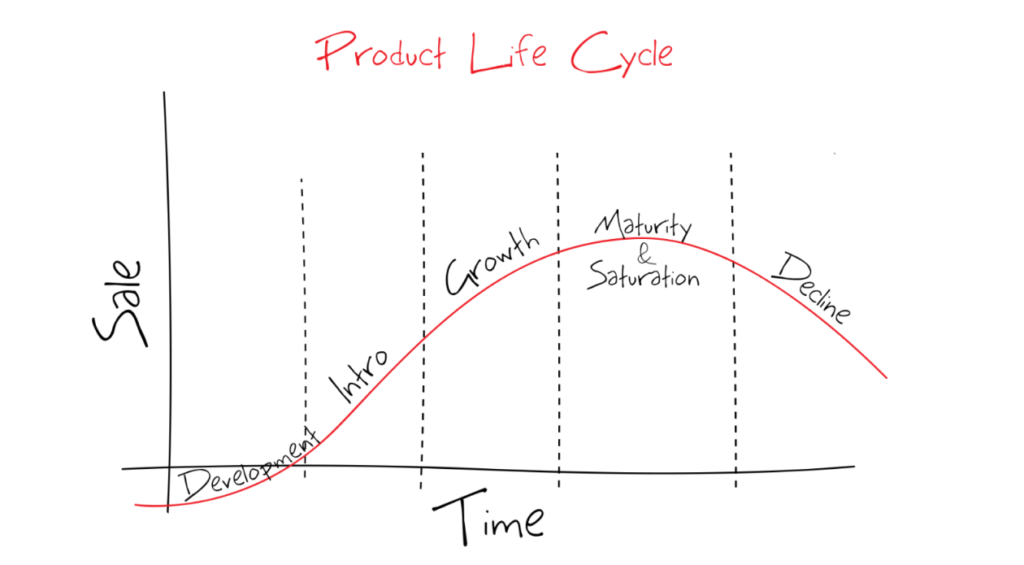
Product Life Cycle (PLC) is the various stages a product goes through when introduced into the market until its retirement. It encompasses the analysis of the whole lifespan of the product. PLC helps companies track the product’s health and make an informed strategic decision on how to price, promote, expand, and reduce its cost. Based on the product’s stage, product managers have to use different skills to support the product.
Watch the product life cycle, but more important, watch the market life cycle.
– Author: Philip Kotler
What are the different stages in Product life cycle ?
Let us understand the different stages of the product life cycle, and then we can look at an existing product in the market to better understand the concept. I have used various examples while explaining the different stages of the Product life cycle. And in the end, we will deep dive into the product lifecycle phases of Facebook.
1. DEVELOPMENT
Product development is the first stage of the product life cycle. It is the Research and Development phase before the introduction of the product in the market.
Market research, benchmarking, Competitive Analysis, Prototypes Design, Prototype testing, Product strategy are all part of this stage of the product life cycle. As the product is still in R&D, companies have to spend a lot of money with no revenue. Based on the complexity of the product, its development may take a long time and massive funding. Due to lack of resources or budget to build the product, not all the innovation idea crosses the “Valley of death” (a commonly used metaphor to signify lack of resources)
Role of Product Manager in the Development Stage
During the development stage of product life cycle , the product managers will layout out the product strategy, create a product road map, outline the product’s functional requirement, make prototypes, validate the product, and prepare for the launch. They work with the stakeholders and team throughout the different phases of product development.
Highlights of the Development Stage
- Increase in investment and no sales as Product is not in the marketplace
- Market research and Competitor analysis
- Development and test product effectiveness
- Strategy for Product launch and commercialization
Next Gen iPhone is currently in the development stage; there is already a buzz about OLED display, 5G connectivity, and enhanced camera specs. Apple will reveal it during its annual event in Sept 2020
2. INTRODUCTION
The Introduction stage of the product life cycle is when the product gets launched or introduced in the market. During this stage, the product is advertised and promoted to increase awareness and establish a good consumer base. The product pricing strategy plays a very crucial role during the introduction stage to gain market confidence. It is also known as New Product Pricing. Some of the popular pricing strategies are Market-Skimming Pricing and Market-Penetration Pricing strategy.
Popular Pricing Strategies
In the Market-Skimming Pricing strategy, the product price point is set high to get maximum revenue from the customer segment who are willing to pay. The price is then strategically and stepwise reduce to skim maximum profits layer by layer through each customer segment.
One of the familiar players to use this strategy is Apple. Before the new iPhone release, there is a buzz created around the new features, to skim the cream customers willing to pay a higher price to get their hands on the product. In the later phase, they launch a SE version, which is a much cheaper version targeting a specific customer segment.
In the Market–Penetration Pricing strategy, the product price is set low to penetrate the market quickly and deeply at the expense of revenue. It is to attract the customer away from the competitors. This strategy is also known as Predatory Pricing. For example, Amazon, Uber attracted and built a loyal customer base by offering a low price point.
Highlights of the Introduction Stage
- Increase in the marketing and advertising cost to improve product awareness
- Low Sales volume as the product is new to the market and consumer base has just started to grow
- Limited profits due to low sales volume and awareness of the product
- Limited competition if the product is a niche giving the first-mover advantage.
In November ’19, Tesla finally unveiled its Cybertruck, targeting a new market segment using a skimming Pricing strategy. The electric-car maker followed a similar approach with its Model 3 sedan, releasing more expensive — and more profitable — versions before the least expensive trim.
3. GROWTH
The growth stage of the product life cycle is also known as the “Take-off” stage. It is when the market has reacted favorably, and the market value of the Product is increasing. Investors are willing to invest in the Product. And there is a gradual rise in the sales curve due to increasing popularity and consumer demands (refer to the chart at the top)
In this stage, the product distribution and reach are expanded further by investing in advertisement campaigns and promotions for your target audience. The advertisement strategy would depend on the kind of Product, i.e., B2B or B2C. It could be advertising through digital channels like Instagram, Twitter, etc., or traditional endorsements such as TV commercials, Radio Channels & Newspapers.
There is also an increase in competition as the new players want to set their foot in the developing market. For example, the telemedicine world’s whole revolution fueled further with COVID, highlighting all telemedicine companies. As investors saw an opportunity and are willing to invest in the telemedicine and virtual care space now, many new players have emerged in the market.
During this phase, the product managers focus on enhancing and adding new features to sustain growth and increase the business substantially. They can use a data-driven approach and identify new features by analyzing customer feedback and market response.
Highlights of the Growth Stage
- Increase in the awareness of the product due to advertisement campaigns and promotions
- Increase in sales and reduction in the production cost leads to more profitability
- Increase in competition as new players want to set foot on the developing market
- Increase in reach of the product by Introducing additional features to tap the untapped customer segment
Tiktok is the most downloaded App Store and is one of the fastest-growing social media platforms. As per the latest stats, Tiktok has more than 2 Billion times downloads worldwide
4. MATURITY
As the Product matures, it becomes more profitable as the cost of development and marketing significantly reduces. However, the growth of the Product starts showing signs of saturation or slow down. During the product life cycle’s maturity stage, the Product’s sales will be at its peak, and the competition will increase substantially.
To survive against the fierce competition and maintain profitability, the companies have to work on consistent product innovation. It is also known as the Product Extension strategy. It is where the product managers play a vital role in creating differentiation in the Product. In recent times, Instagram, a leading social media platform, has added features like Stories and Reels to take on its competitors.
Some of the common Product Extension strategies are enhancing the features & services, new advertising campaigns, revitalizing the brand packaging, targeting new customer segments to engage their consumers, and staying profitable.
Highlights of the Maturity Stage
- A Peak in the sales volume as the market starts showing sign of saturation
- Increase in competition leading to new features and reduce costing of the product
- Increase in market share by differentiation (i.e., adding features, targeted marketing)
- A Decrease in profits towards the end of the maturity cycle.
Netflix was founded in 1997 and initially started with DVD rental services. The company continued to evolve and, in 2007, introduced the streaming services. With 182 million paid subscriptions and low fixed cost Netflix is dominating the market but faces strong competition from amazon prime, Disney. With the COVID acting as a catalyst, it’s subscription and stock price has seen a consistent increase in the last few months
5. DECLINE
In the Maturity stage of the product life cycle, the revenue and user base starts to decline. It can be because of the new competitive products in the market or consumer losing interest. If you refer to the chart, this phase shows a decline in sales and profit.
The companies reassess their Product to add additional features between the Maturity and Decline phase or eventually decide to sunset the Product. It is crucial to understand if the Product has reached the decline stage or this is just a temporary dip in sales, and therefore, deciding to use Product Extension Strategies to survive in the market.
In this phase, the product managers focus on expanding the company portfolio and leveraging the existing consumer base or working to tap an entirely new market. One example is of a leading tech company Microsoft that shifted the focus to the cloud and subscription model instead of making smartphones and recorded remarkable growth.
Highlights of the Decline Stage
- Decreasing sales and profits due to the decline in the market of the product
- Reducing the production and maintenance cost to make a profit even when the sales decline
- The Decision to Discontinue the product and to get most out of it by mergers and acquisitions
Though the Product life cycle comes with its advantages like understanding the market’s product performance, it is too neat a picture. Many products might enter the introduction stage rather than show an exact growth phase; the sales start to decline. It is dependent on the sales data, and any data fluctuation may lead to inaccuracy and wrong decisions. How best it will fit will depend on multiple factors like the market and product type. As a product manager, we should adept at changing the strategies based on the Product’s market response and adaptation.
What is the difference between the product life cycle and product development life cycle?
Product development is the first stage in PLC. The Product life cycle is the Product’s life span from conception to retirement, focused mainly on product introduction, positioning, performance, and growth. However, the Product development life cycle is different phases of the Product from idea inception, development to commercialization, focused mainly on building the right Product and the Product right.
I Will discuss the Product Development Life Cycle in my next blog. Meanwhile, take some real-life examples and map them to the different phases of the product life cycle. As always, I will be more than happy to discuss this. You can connect with me at @_IamAkansha_.
To get the latest Product Management blogs and NEWS delivered to your Inbox. JOIN THE NEWSLETTER.